With the advancement of healthcare technology, the efficiency of care delivery increased; however, with it, the threat of security breaches also went up. This is where following compliances like HIPAA, HITECH, and GDPR becomes important and plays a crucial role in data security and privacy.
That’s why strong security measures are required to protect the PCM software and for patient information security. Having end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security assessments are just a few of the steps you need to take to keep data safe and private.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the critical security aspects of principal care management software, from regulatory requirements to best practices. Whether you’re a provider, administrator, or IT specialist, understanding these safeguards is key to protecting your patients and your practice.
Let’s explore what it takes to build a secure and reliable PCM system in today’s healthcare environment!
Whenever healthcare providers share data with each other, there is always the risk of external intervention during the data transmission or even when at rest. Here, what makes the data safe to transmit and minimizes the risk of intervention or data breach is end-to-end encryption. With unique and encrypted keys, the data can only be accessed by providers with their unique decryption keys.
But only encryption is not enough, as many times the threat is not external and can come from inside the organization. In a healthcare organization, there are multiple departments with many roles, so it is not secure to give complete access. This is where role-based access control comes into the picture and gives only needed access and limits the spread of information. With this, you can effectively control unauthorized access and sharing of information outside the organization.
Another thing that controls access authorization is multi-factor authentication, or MFA. With MFA, you have to provide something additional along with the password, such as biometric scans, additional keys, or an access device. Doing this ensures that only authorized personnel can access the files, and no one can enter them by hacking the password.
In addition to this, performing regular audits of access logs, which are recorded during the entry, can show you any suspicious activity. With this monitoring, the access time and reason can be easily tracked, and you can learn of any unauthorized or outside intervention in the system.
With principal care management software, you enter into digital healthcare, and here, you need to follow the needed compliances that enhance data security and privacy further. Some of the most widely known and used compliances are HIPAA, HITECH, and GDPR. These compliances give the rules and regulations for data storage and sharing, and even penalties if any of it is violated.
So, you need to have software that supports all of these compliances to protect patient data, but it is not only for principal care management data security. Not having HIPAA-compliant PCM software can lead to severe legal consequences and hefty fines. Additionally, doing regular risk assessments makes it possible to spot irregularities in your system and identify security gaps and bugs.
With all this, you need to ask for a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with the software vendor. A BAA protects both healthcare providers and software vendors by ensuring HIPAA compliance when handling patient data. It defines security responsibilities, limits liability, and clarifies legal obligations. Providers stay protected if a vendor mishandles data, while vendors get clear guidelines to avoid compliance risks. It’s a legal safeguard for both sides and makes sure that you receive robust data protection principal care management software.
When it comes to storing sensitive healthcare data, security is not a luxury but becomes a necessity, and cloud-based storage solutions fulfill this for you. It comes equipped with features such as data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and real-time monitoring.
Along with this, another crucial factor is data backup and disaster recovery plans, as losing patient data during a system crash or a cyber attack can be a nightmare. However, this can be avoided with scheduled backups, both online and offline, to ensure that even if the system fails, another copy is available to keep operations running smoothly.
Patient data privacy is as important as keeping it safe and secure, and here, data masking of the patient data helps. This helps in hiding the original details, makes the user information anonymous, and allows healthcare organizations to use the data responsibly without compromising confidentiality.
Apart from this, physical security matters too. Servers should be kept in secure facilities with strict access controls, surveillance, and environmental protection. This guards against breaches and natural disasters, ensuring healthcare data stays safe and accessible when needed.
Keeping software updated is not just about getting the latest features; it is also important for keeping the data safe and secure. With advancing technology, hackers are also advancing their ways to get into your security network. This is where regular updates help you out and get your system ready to defend against attacks with the new security patches. When this is done, the bugs and loopholes are fixed, and cyber attackers can not exploit the vulnerabilities to enter the data network.
Another part of managing software security is proactive vulnerability scanning and penetration testing. As the name suggests, scanning your security network periodically helps identify gaps and loopholes that can compromise the system’s security. Moreover, with penetration testing, you can proactively look for the bugs and patch them before any cyber attacker exploits them.
After the identification of the security vulnerabilities, the next step is to record and address them as per their severity and patch them. Here, you need to create a report that contains all the vulnerabilities from high to low priority. This gives you an effective way to patch the gaps in the security network and address all the vulnerabilities without missing any.
As the system updates are the responsibility of your software vendor, it is vital to know what security practices they perform. Having transparency is important as it depends on the vendor’s security practices, and how secure the patches are for the software.
When it comes to protecting sensitive data, employees can be your greatest asset or vulnerability. With a single poorly trained employee, your whole security can be compromised, no matter how advanced the technology is. This is why you need to train your employees in data security best practices and ensure they know a threat when they see it. Also, they should know how to properly handle the data and keep the passwords safe and secure.
However, a single session on this is not enough, and repeated webinars and awareness campaigns on cybersecurity are needed. With changing cyber threats and means of entering the data networks, your staff needs to be aware of the latest changes in technology.
Furthermore, having policies such as strong passwords, avoiding repeated passwords, and regular password changes is essential to avoid data breaches. Additionally, classifying data as per confidentiality and keeping it encrypted is also essential to avoid unnecessary disclosure and data spread. These practices make sure that access and data handling are strictly controlled, and patient information security is ensured, and it remains private.
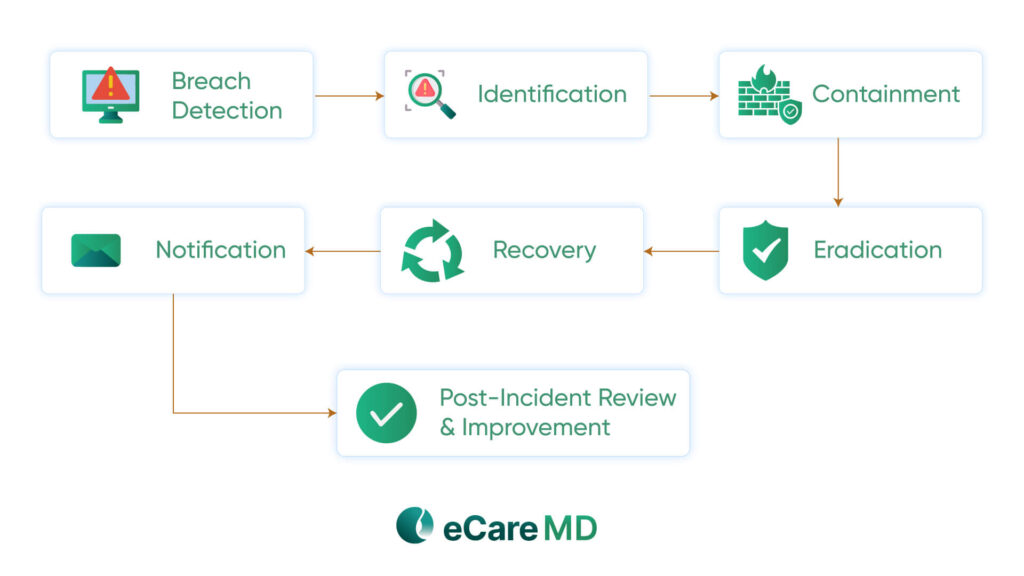
When your system is breached, every second counts, and it is essential to react quickly and contain the damage. For that, you need to develop an effective incident response plan, which involves several steps. The first one is preparing a designated team for the scenario, and the next is detecting and monitoring every system to identify a breach.
Next step is to contain the breach to avoid damage to other systems and isolate the affected system from others. With this done, next comes the eradication of the virus or the malware that is the root cause of the breach, as well as resetting passwords and access. Data recovery and the ability to bring the systems online become possible after the root cause has been eradicated.
After the incident, analysis is essential to make improvements and know what measures worked best. This helps identify the gaps and patch them instantly, but after an incident, one more step is crucial, and that is breach notification. Notifying the affected individuals and the regulatory bodies, such as the Health and Human Services (HHS), about the incident is important.
Last but not least is having a strong communication plan; disruption of communication during the breach can lead to severe consequences. With communication, your team can quickly know what to do without panic setting in and can effectively respond to inquiries about the situation. So, keeping communication smooth is crucial in a data breach or cyberattack.