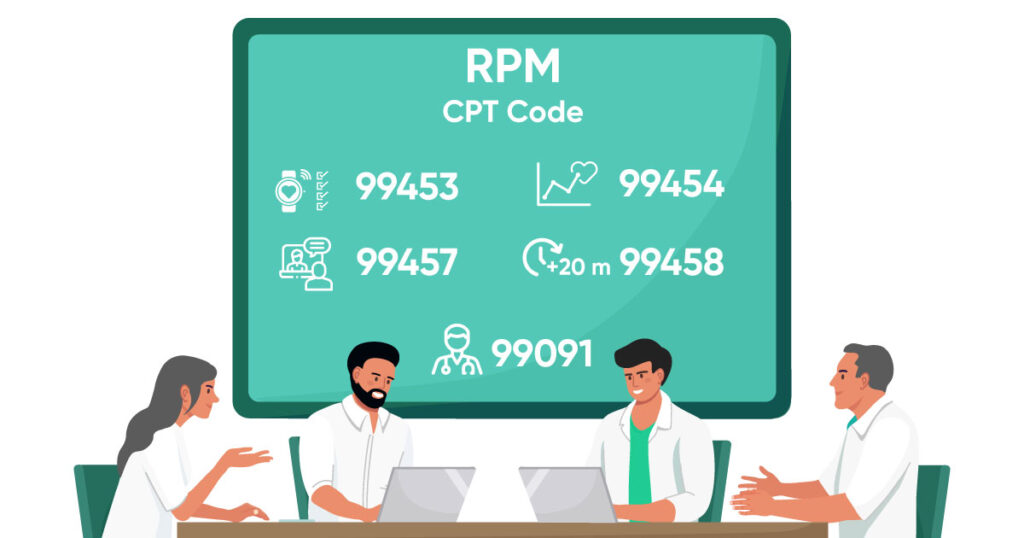
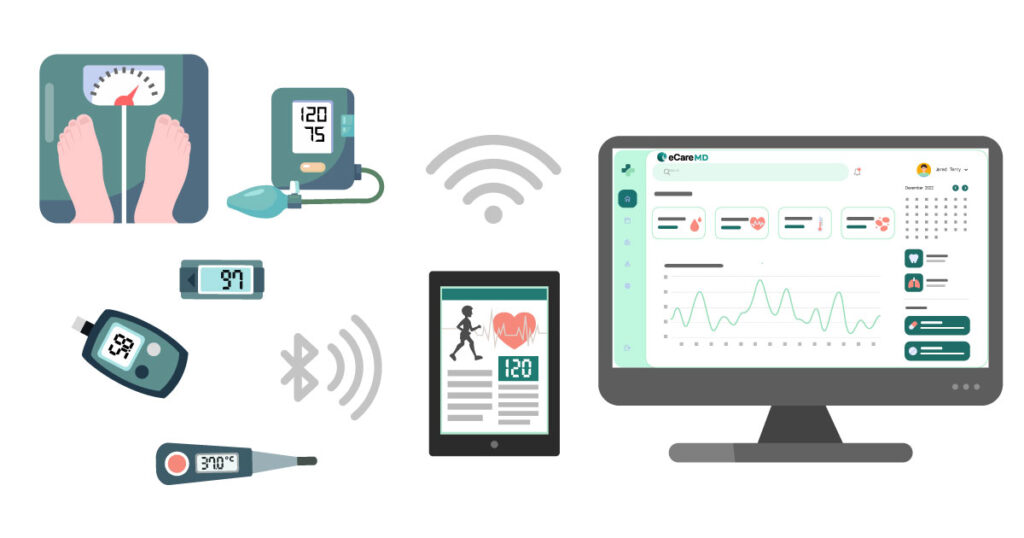
Data-driven healthcare practices have increased the patient engagement by 80%!
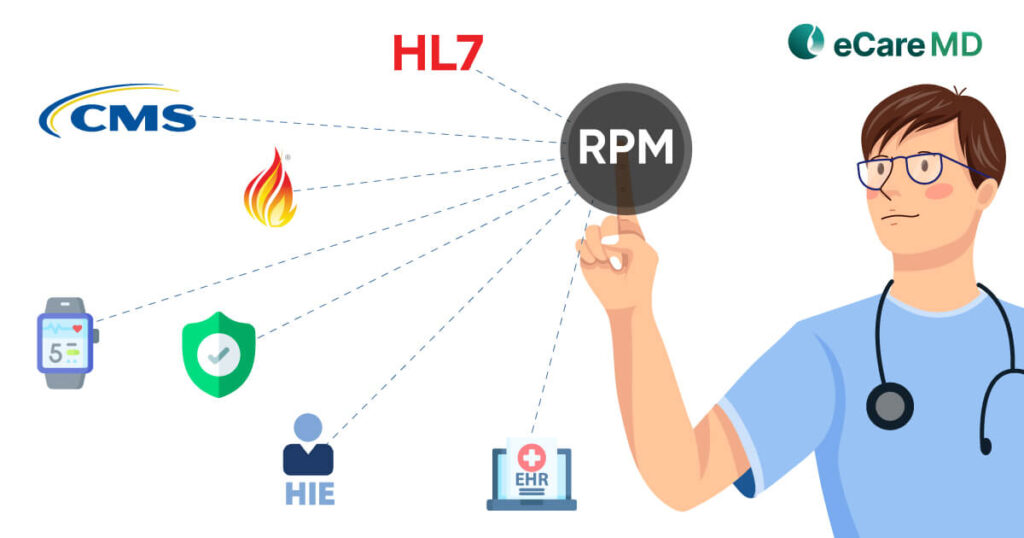
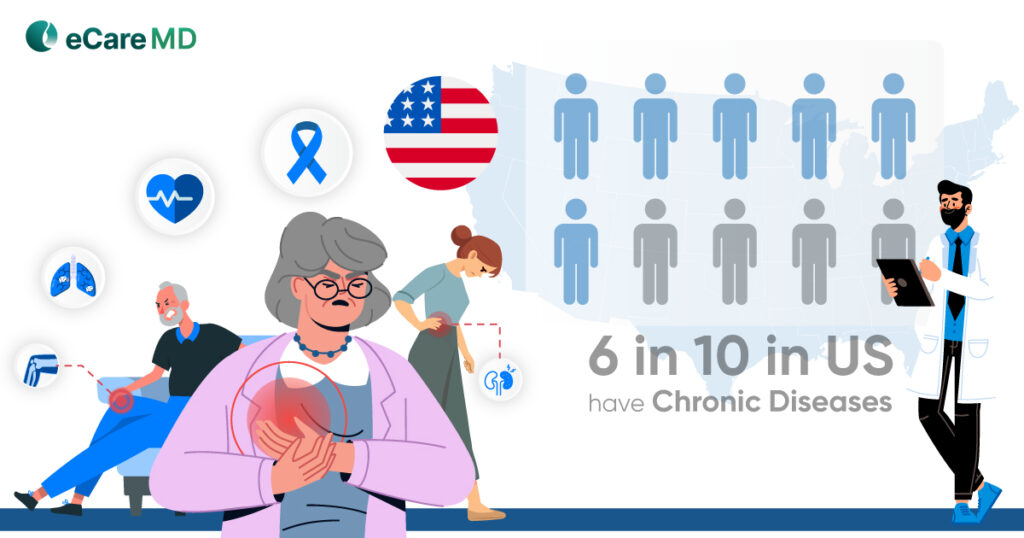
While many practices are adapting healthcare technology to reduce the pressure and cost involved in care, all the systems need to work in sync to make the program work. The crucial cornerstone involved in CMS RPM program implementation is interoperability and integration.
Understanding Interoperability

1. HL7 (Health Level Seven): Widely used set of standards for the smooth exchange, integration, sharing, and receiving of electronic health information.
2. FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources): FHIR is again a set of standards for the smooth exchange and integration of electronic health information. However, it is more flexible and focuses on modern web standards that make it easy for program implementation.
3. DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine): Medical images and reports are crucial for care delivery, and the DICOM standard helps providers achieve that in the digital care landscape. Following these standards ensures interoperability among various imaging devices and picture archiving and communication systems (PACS).
Exploring Integration in CMS RPM Programs
Challenges Without Interoperability and Integration
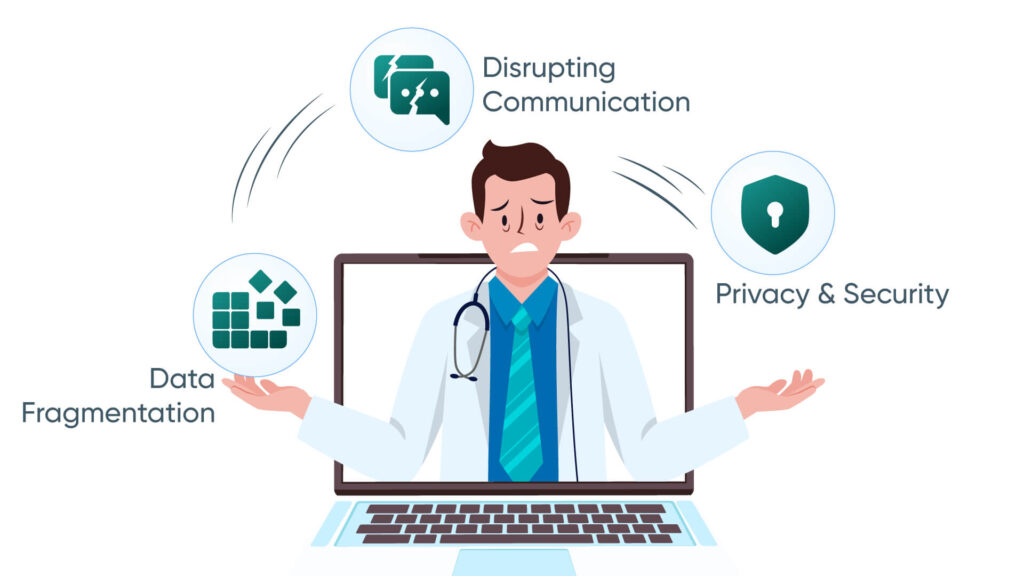
Key Components of Interoperability in CMS RPM

1. Standardized Data Formats and Protocols: Following standardized data formats and protocols like FHIR and HL7 can help you make your systems interoperable. These protocols will further reduce the risks of data fragmentation and increase accuracy while transmitting data.
2. Health Information Exchange (HIE):HIE plays an important role in facilitating interoperability in the program through a secure network. It does this by enabling data aggregation and sharing to give providers a complete picture of the patient’s health. Along with that, it also solved the compatibility issues with standardized communication standards and empowered care coordination.
3. Compatibility with RPM Devices and Systems: Being a provider, you probably know the importance of compatibility with RPM devices and various healthcare systems for smooth operation and care delivery. There are certain regulations that CMS has set off the RPM program to ensure data privacy and integrity. Furthermore, compatibility with devices and systems ensures smooth data exchange and adds the factor of real-time monitoring and personalized care.
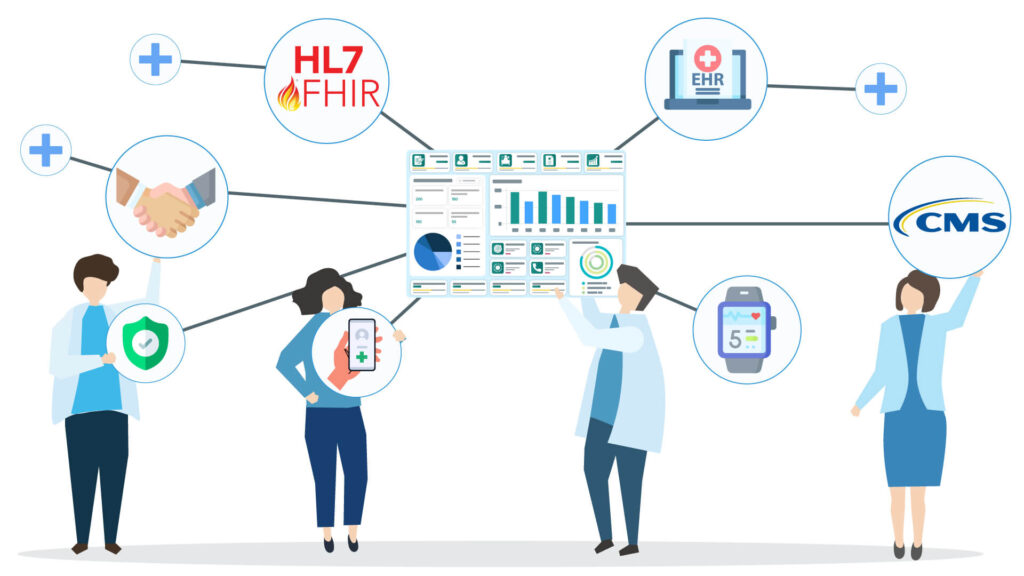
Importance of Integration in RPM Programs
Best Practices for Implementing Interoperability and Integration

1. Collaborative Approach: Implementing interoperability and integration is a collaborative effort. Collaborate with all the healthcare stakeholders, understanding all their needs, and curate an approach accordingly to make the healthcare system interoperable.
2. Adherence to Industry Standards: Another best practice widely used in CMS RPM program implementation is to adhere to the regulatory standards. Utilize industry standards such as HL7 and FHIR to ensure the data exchange is seamless across different healthcare systems.
3. EHR Integration: To increase data accuracy and standardized format, ensure your RPM system seamlessly integrates with the EHR systems.
4. CMS Compliance: As the RPM is initiated by the CMS and also covers most of the healthcare costs, compliance with RPM regulations and guidelines can smooth the implementation of your RPM program.
Future Trends in Interoperability and Integration for CMS RPM
Conclusion
In a nutshell, the interoperability and integration in the CMS RPM program ensures that all the essential elements for providing virtual care and monitoring are imbibed. It encourages data-driven practices in healthcare and contributes significantly to improving care coordination. All of this directly impacts the health outcomes of patients and helps in reducing the overall cost of care.
So, if you are a healthcare provider planning to start your own CMS RPM program, then let this blog be your guide to its successful implementation with interoperability and integration.
Frequently Asked Question’s
There are several key standards used in healthcare data exchange, but some of the most prominent include:
- HL7 (Health Level Seven): A set of international standards for exchanging electronic health information.
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources): A newer HL7 standard that provides a flexible and modern approach to data exchange.
- CDA (Clinical Document Architecture): A standard for exchanging clinical documents in a structured format.
Healthcare organizations can ensure data security and privacy during integration processes by:
- Implementing strong access controls to limit who can access sensitive data.
- Encrypting data at rest and in transit.
- De-identifying data whenever possible to minimize privacy risks.
- Regularly monitoring and auditing systems for security vulnerabilities.
- Educating staff on data security best practices.
Common integration challenges in CMS RPM programs include:
- Data format incompatibility between CMS and RPM systems
- Difficulty synchronizing content updates across platforms
- Security concerns around managing access and permissions
These challenges can be overcome by using standardized data formats, implementing robust synchronization processes, and establishing clear access control policies.
- Real-time patient monitoring by clinicians
- Improved medication adherence tracking
- Better care coordination across providers
Here are some potential risks of inadequate interoperability and integration in RPM programs:
- Data inconsistencies between programs: If RPM programs can’t share data effectively, it can lead to inconsistencies and inaccuracies in the overall data picture.
- Difficulty sharing data and workflows: Without good integration, it can be difficult to share data and workflows between different RPM programs, hindering collaboration and efficiency.
- Increased complexity of system management: In a siloed system with poor integration, managing multiple RPM programs can become more complex and time-consuming.
When selecting interoperable solutions for RPM programs, healthcare providers should consider:
- Compatibility with existing EHR systems to minimize data silos.
- Open data standards to ensure seamless exchange of patient data.
- Strong security measures to safeguard sensitive patient information.
Healthcare organizations can measure the ROI of interoperability and integration in RPM programs by comparing the program’s quantifiable benefits, like reduced readmissions, to the investment in making those systems work together. This ROI can be calculated as a percentage using the following formula: ROI = (Outcomes – Costs) / Costs * 100.
In simpler terms, ROI helps assess if the upfront investment in making different healthcare systems compatible yields financial benefits through better patient outcomes.