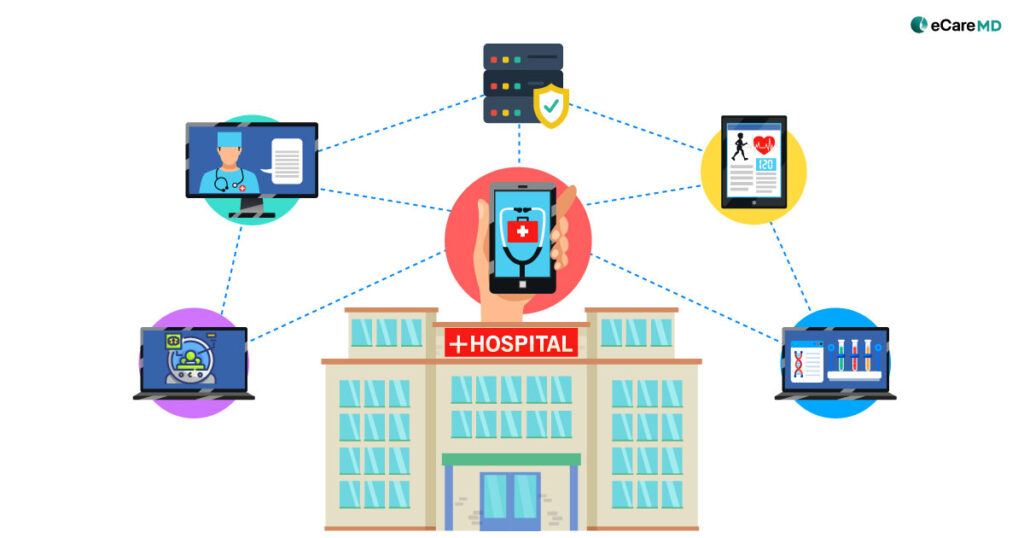
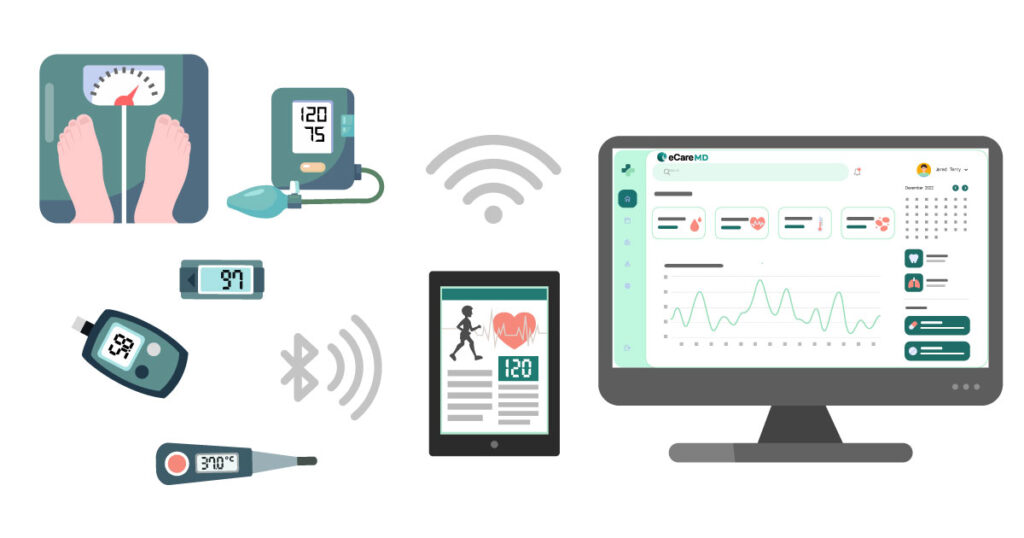
As healthcare practices are moving towards a digital healthcare landscape, don’t you think data is becoming the starting piece of this large puzzle?
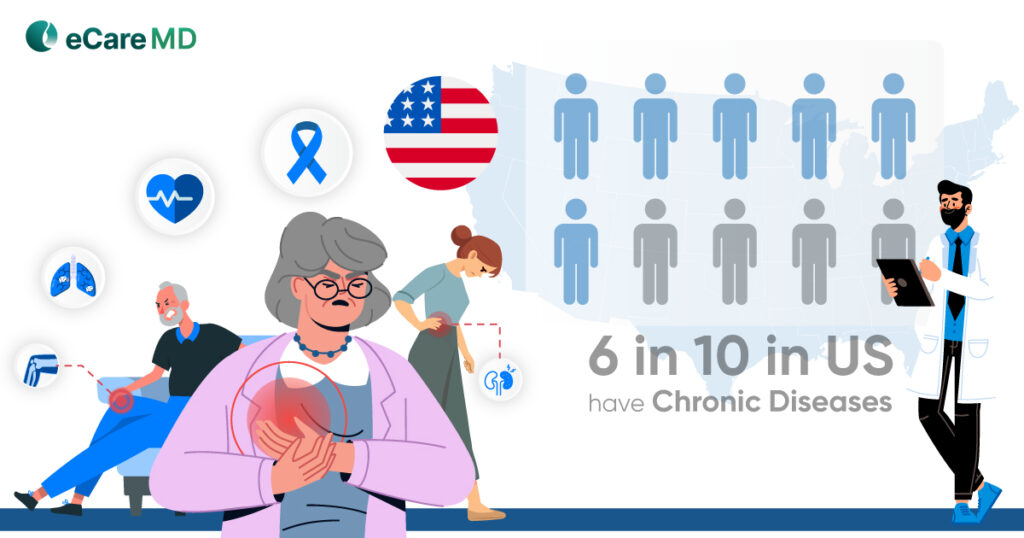
Interoperability in healthcare has encouraged data-based practices, especially in chronic care management software. Since more than half of the aging population struggles with at least one chronic condition, it is bound that the chronic care management program will play a revolutionary role in shaping the future of healthcare.
To prepare for the future, change has to start today, and technology is making that happen in the modern-day healthcare landscape. In simple terms, interoperability is the nervous system facilitating smooth data exchange in healthcare. Afterall, its importance in the changing landscape has inspired more than 84% of the hospitals to adopt interoperability standards like HL7 and FHIR.
So, in this blog, let’s see how interoperability is facilitating smooth data exchange in chronic care management software.
Advantages of Interoperability in Chronic Care Management

1. Care Coordination: Interoperability allows healthcare systems to exchange important health information in real-time. This enhances coordination between care team members, allowing them to work together effectively on one goal to improve patient health outcomes.
2. Real-time Data Sharing & Collaboration: Healthcare interoperability solutions in chronic care management allow the authorized user to pull comprehensive patient data from disparate servers, allowing real-time data sharing. Combining this with integrated chronic care management software, data can be easily added to the patients’ EHRs, enhancing collaboration amongst various team members. This speeds up care delivery with accuracy in data, which directly enhances care coordination, care planning, and the care delivery process.
3. Comprehensive Patient Information: Real-time data sharing between remote monitoring devices and desperate provides complete patient data. Its integration with EHR systems enables providers to have a complete picture of a patient’s health history. This helps in the curation of personalized care plans with a holistic approach to providing quality care services.
4. Data Accuracy: Data accuracy plays an important role in every aspect of chronic care management programs. The accuracy of data facilitates providers to make informed decisions in care planning and care delivery. Along with that, the accuracy of data also acts as an action pointer to intervene and provide preventive care to improve health outcomes.
Technical Aspects of Interoperability in CCM Software
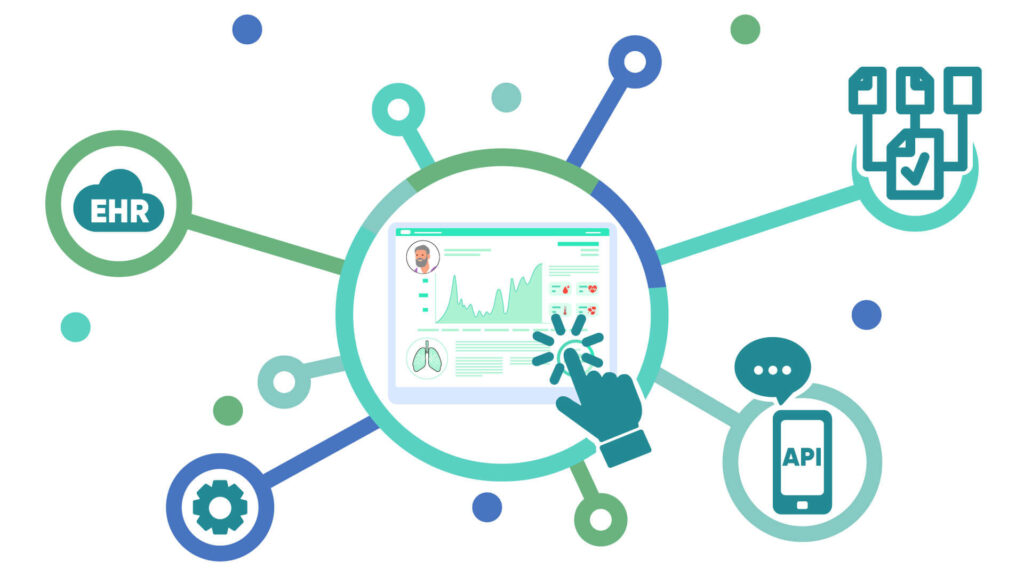
Interoperability in chronic care management software is something that keeps patients and providers in the loop during the entire care journey. To achieve interoperability in the chronic care management software, its technical aspects need to be sophisticated and easy, even for disparate systems to understand.
1. Standardized Data Formats and Protocols: One technical aspect that needs to be standardized is the data formats and protocols followed to achieve interoperability in CCM software. If one set of standardized data formats is followed across healthcare systems, it becomes easier for the system to understand and exchange data accurately. Though some of the set standards, like HL7 and FHIR, are making efforts to define the standardized formats to achieve interoperability in healthcare, it is easier said than done. A standardized format for data is important for seamless sharing of data and improving all the processes of providing care.
2. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): Along with the standardized formats, developing APIs is clinically important to enable the systems to process the requests to get the desired results. APIs facilitate secure data, which allows the integrated CCM software to comfortably connect with other systems like EHRs, billings, RPM, etc. The role of APIs is like that of a digital waiter that provides a common language for the development of robust ecosystems around the CCM software. This ultimately leads to providing better care facilities with improved collaboration and defining the workflow to achieve the set goals.
3. Ensuring Compatibility With EHRs (Electronic Health Records): The significance of EHRs in a healthcare setting, especially in chronic care management, is vital to managing patient data. Since interoperability deals with the sharing of this data from different systems, it is important to ensure that the interoperability in integrated chronic care management software is compatible with EHRs. It enhances care coordination and acts as a point of reference for providers to make informed and evidence-based decisions. Some of the important things to consider while ensuring its compatibility are seamless integration, real-time data sharing, standardized data formats, and patient engagement features like appointment scheduling.
Overcoming Challenges
Healthcare interoperability solutions in chronic care management are crucial for important data exchange and to drive data-based decisions. However, the road to achieving interoperability for chronic care management software is challenging.
1. Privacy and Security of Patient Data Exchange: The healthcare industry is prone to cyberattacks, and gaps in the data exchange process can lead to data thefts, manipulations, etc. This can increase the chances of misdiagnosis, leading to poor patient health outcomes and even population health mismanagement. That is why it is important to address the privacy and security concerns of patient data. Here are some of the key measures to ensure security and privacy in interoperability:
- Data Encryption: Implementing strong encryption protocols like TLS and others to ensure secure data transmission between different systems.
- Secure APIs: Implementing secure and robust APIs to ensure best practices for authentication, authorization, and data transmission.
- Access Controls: Develop and implement a secure access control mechanism for authorized access to patient’s sensitive health information.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence with HIPAA or GDPR regulatory bodies can ensure that effective security and privacy measures are being taken.
- Audit Trails: Conduct regular audits to track and manage all the activities related to data exchange in the healthcare industry. This can help identify any ongoing suspicious activities.
2. Regulatory considerations and compliance in healthcare interoperability: To achieve interoperability in the healthcare system, it has to pass through various aspects like standards, patient privacy, data exchange, etc. Here are some of the regulatory considers and compliance to get into healthcare interoperability solutions:
- HIPAA: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, commonly known as HIPAA, is a US federal law responsible for framing the standards to ensure patient data security and privacy.
- HITECH Act: The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, implemented in 2009, is a law to maintain the integrity of the use of health information technology.
- CMS Regulations: The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services has set some regulations under which the CCM program falls. Following its regulations is crucially important for the success of the CCM software.
- ONC Regulations: The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology issues regulations for better use of health information technology and ensures that the healthcare system is interoperable.
- FHIR: Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources is a standard for exchanging information electronically. Compliance with FHIR standards can ensure a smooth exchange of information between disparate systems.
Download Free Checklist for Necessary Compliances and Regulatory Requirements
Download now3. Resistance to Adopting Interoperable Solutions: The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, and changes brought by technology can be overwhelming for healthcare providers. Adopting this change can be challenging for many healthcare organizations as they might face resistance from their staff. To overcome these challenges, here are some strategies that can be implemented:
- Education and Awareness: Educating everyone about the benefits of interoperability solutions can be a helpful way of adopting new solutions in enhancing care facilities.
- Standardization and Regulations: Encouraging the implementation of set standards across systems can promote interoperability, further helping the providers to adapt to the change easily.
- Training and Support: Provide comprehensive training to the users to help them adapt to the solution easily and how it can help them in simplifying their work.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a cost-benefit analysis for the solution for long-term financial advantages. This can make the board members embrace the chance with open arms.
Conclusion
Chronic care management programs rely heavily on the interoperability of the CCM software for their success. It not only fosters the smooth exchange of accurate data and information but also helps in driving data-based decision-making that ultimately results in improved patient outcomes.
However, adopting interoperable CCM software is in full swing to encourage more data-driven healthcare practices. Though driven by challenges, achieving interoperability in CCM software can enhance all the processes and aspects of providing healthcare facilities.
Moving ahead in this digital era of healthcare practices, healthcare interoperability solutions will play a huge role in the future success of CRM software. Since the aging population will soon be aged, treating them with accurate diagnosis will be crucial because of healthcare interoperability.
Free Guide to Unlocking the Potential of Interoperability for Chronic Care Management
Frequently Asked Question’s
Some of the major challenges in achieving interoperability in healthcare are:
- Inconsistent Data
- System Compatibility Issues
- Information Privacy
- Large Data
- Duplicated or Fragmented Health Data